About
102
Publications
9,666
Reads
How we measure 'reads'
A 'read' is counted each time someone views a publication summary (such as the title, abstract, and list of authors), clicks on a figure, or views or downloads the full-text. Learn more
2,074
Citations
Introduction
Publications
Publications (102)
An odor sensor is a device for detecting target odors within a mixture, used in many fields including medical diagnosis. Electronic noses are networks of olfactory sensors, consisting of a surface whose properties are modified in the presence of odors, coupled with a measurement system. Their olfactory signature is analyzed in comparison with datab...
An odor sensor is a device for detecting target odors within a mixture, used in many fields including medical diagnosis, Electronic noses are networks of olfactory sensors, consisting of a surface whose properties are modified in the presence of odors, coupled with a measurement system. Their olfactory signature is analyzed in comparison with datab...
Le diagnostic et le suivi de pathologies, dont les cancers et les pathologies infectieuses, représentent des enjeux majeurs de santé publique. Les odeurs corporelles sont caractéristiques de chaque individu, et dépendent de son profil génétique et de son état physiopathologique. La présence d'odeurs corporelles spécifiques a été identifiée dans plu...
Pulmonary arterial hypertension {PAH) is a rare progressive disease due to dista lvascular remodeling, leading to right heart failure and death. PSGR is an olfactory receptor {OR) that has been recently detected in peripheral tissues. Moreover, PSGR overexpression is associated with pro-proliferative phenotype in prostate cancer. Since PAH vascular...
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare progressive disease due to distal vascular remodeling, leading to right heart failure and death. PSGR is an olfactory receptor (OR) that has been recently detected in peripheral tissues. Moreover, PSGR overexpression is associated with pro-proliferative phenotype in prostate cancer. Since PAH vascular...
Two olfactory receptors (ORs), mouse M71 and chimpanzee OR7D4, were immobilized onto synthetic diamond transducers surfaces. 6His tagged M71 (6His-M71) was grafted using covalent attachment of nitriloacetic acid (NTA) as chelating agent, which could bind the 6His tagged receptor through nickel ions. OR7D4 was grafted through covalent bonding of hex...
Cell membrane proteins are involved in a variety of biochemical pathways and therefore constitute important targets for therapy and development of new drugs. Bioanalytical platforms and binding assays using these membrane protein receptors for drug screening or diagnostic require the construction of well-characterized liposome and lipid bilayer arr...
Le diagnostic et le suivi de pathologies, dont les cancers et les pathologies infectieuses, représentent des enjeux majeurs dans le domaine de la santé. De nouveaux nanobiocapteurs, dont les éléments sensibles sont des récepteurs olfactifs, donnent la possibilité de développer des dispositifs de détection performants, bon marché, permettant une mes...
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is due to progressive obstruction of pulmonary arteries, thus leading to right heart failure and death. Breath volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can discriminate PAH and controls. Thus, a unique breath-print of PAH is detected using an artificial nose. VOCs target olfactory receptors (ORs) in olfaction. Interes...
This chapter describes the main characteristics of olfactory receptor (OR) genes of vertebrates, including generation of this large multigenic family and pseudogenization. OR genes are compared in relation to evolution and among species. OR gene structure and selection of a given gene for expression in an olfactory sensory neuron (OSN) are tackled....
Le diagnostic et le suivi de pathologies, dont les cancers et les pathologies infectieuses, représentent des enjeux majeurs dans le domaine de la santé. De nouveaux nanobiocapteurs, dont les éléments sensibles sont des récepteurs olfactifs, donnent la possibilité de développer des dispositifs de détection performants, bon marché, permettant une mes...
Une nouvelle génération de biosenseurs, les nanobiosenseurs, dont les éléments sensibles sont des récepteurs olfactifs, peut déboucher sur des nez bioélectroniques performants, bon marché, permettant une mesure quantitative et directe, sans marqueur. Ils pourront en particulier être intégrés dans des instruments pour le diagnostic médical non invas...
Bioelectronic noses can utilize olfactory receptors (ORs) as recognition elements. This chapter describes biochemical characteristics of these OR proteins. ORs being G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are integral membrane proteins composed of seven transmembrane spanning helices. In mammals, there exist as many as 1,000 OR genes accounting for ab...
Mechanical properties of nano-sized vesicles made up of natural membranes are crucial to the development of stable, biocompatible nanocontainers with enhanced functional, recognition and sensing capabilities. Here we measure and compare the mechanical properties of plasma and inner membrane nanovesicles ∼80 nm in diameter obtained from disrupted ye...
Olfactory receptors (ORs) are expressed in the olfactory epithelium, where they detect odorants, but also in other tissues with additional functions. Some ORs are even overexpressed in tumor cells. In this study, we identified ORs expressed in enterochromaffin tumor cells by RT-PCR, showing that single cells can co-express several ORs. Some of the...
Olfactory receptors (ORs) constitute the largest multigenic G protein-coupled receptor family, and are involved in the recognition of thousands of odorant molecules. However, if most of these ORs are identified on the basis of their DNA sequences, they are still unmatched to their natural ligands, and their deorphanization remains a challenging bot...
The neuronal olfactory epithelium undergoes permanent renewal because of environmental aggression. This renewal is partly regulated by factors modulating the level of neuronal apoptosis. Among them, we had previously characterized endothelin as neuroprotective. In this study, we explored the effect of cell survival factor deprivation in the olfacto...
Olfactory receptors (ORs) constitute the largest multigenic G protein-coupled receptor family, and are involved in the recognition of thousands of odorant molecules. However, if most of these ORs are identified on the basis of their DNA sequences, they are still unmatched to their natural ligands, and their deorphanization remains a challenging bot...
Hetero- and homo-oligomerization of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) has been addressed in the past years using various approaches such as co-immunoprecipitation, fluorescence resonance energy transfer and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET). Here, we report the methodological details from a previously published study to investigate...
Hetero- and homo-oligomerization of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) has been addressed in the past years using various approaches such as co-immunoprecipitation, fluorescence resonance energy transfer and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET). Here, we report the methodological details from a previously published study to investigate...
Natural vesicles produced from genetically engineered cells with tailored membrane receptor composition are promising building blocks for sensing biodevices. This is particularly true for the case of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) present in many sensing processes in cells, whose functionality crucially depends on their lipid environment. Howe...
Olfactory receptors (ORs) belong to the superfamily of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), the second largest class of genes after those related to immunity, and account for about 3 % of mammalian genomes. ORs are present in all multicellular organisms and represent more than half the GPCRs in mammalian species (e.g., the mouse OR repertoire conta...
We present a procedure that (i) automates the homology modeling of mammalian olfactory receptors (ORs) based on the six three-dimensional
(3D) structures of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) available so far and (ii) performs the docking of odorants on these
models, using the concept of colony energy to score the complexes. ORs exhibit low-sequen...
In this work we present a biosensor based on olfactory receptors as a new bioelectronic device for detecting the
presence and for measuring the concentration of specific odorants. To increase the surface of transducers, and
consequently amplify the electrochemical signal, we generated gold nanoparticles on the surface of gold electrode. The charact...
G-protein-coupled receptor homo-oligomerization has been increasingly reported. However, little is known regarding the relationship
between activation of the receptor and its association/conformational states. The mammalian olfactory receptors (ORs) belong
to the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. In this study, the homo-oligomerization status...
The present work focuses on the development of an immunosensing surface to build a portable olfactory system for the detection of complex mixture of odorants. Homogeneous cell derived vesicles expressing the olfactory receptors were produced and immobilized with efficiency onto a gold substrate through an optimized surface functionalization method.
Native porcine odorant-binding protein (OBP) bears eleven sites of phosphorylation, which are not always occupied in the molecular population, suggesting that different isoforms could co-exist in animal tissues. As phosphorylation is a dynamic process resulting in temporary conformational changes that regulate the function of target proteins, we in...
Native porcine odorant-binding protein (OBP) bears eleven sites of phosphorylation, which are not always occupied in the molecular population, suggesting that different isoforms could co-exist in animal tissues. As phosphorylation is a dynamic process resulting in temporary conformational changes that regulate the function of target proteins, we in...
The animal olfactory system represents the gold standard of biosensors, due to its ability to identify and discriminate thousands
of odorant compounds with very low thresholds. Using olfactory receptors (ORs) as sensing elements instead of chemical sensors,
biosensors would benefit the naturally optimized molecular recognition of odorants to develo...
We report here the results of human olfactory receptor (OR) 17-40 stimulation with some odorants probed by means of the double-channel surface plasmon resonance platform NanoSPR-6. OR 17-40 tagged with N-terminal cmyc sequence was heterologously co-expressed with Galpha(olf) protein in yeast, and receptor-carrying nanosomes were prepared from yeast...
The human olfactory receptor OR 17–40 co-expressed with α-subunit of Golf protein in yeast was attempted as a bio recognition part of impedimetric biosensor. The receptor in its natural membrane environment was anchored to a gold-coated glass substrate modified with thiol-based multilayer. Step-by-step building-up of the OR 17–40 based biofilm was...
We investigate the immobilization of native nanovesicles containing functional olfactory receptors onto gold electrodes by means of atomic force microscopy in liquid. We show that nanovesicles can be adsorbed without disrupting them presenting sizes once immobilized ranging from 50 nm to 200 nm in diameter. The size of the nanovesicles shows no dep...
The molecular mechanisms underlying odorant detection have been investigated using the chip based SPR technique by focusing on the dynamic interactions between transmembrane Olfactory Receptor OR1740, odorant ligands and soluble Odorant-Binding Protein (OBP-1F). The OR1740 present in the lipid bilayer of nanosomes derived from transformed yeasts sp...
In the SPOT-NOSED European project, nanoscale sensing elements bearing olfactory receptors and grafted onto functionalized gold substrates are used as odorant detectors to develop a new concept of nanobioelectronic nose, through sensitive impedancemetric measurement of single receptor conformational change upon ligand binding, with a better specifi...
This work shows the feasibility of an olfactory biosensor based on the immobilization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast cells genetically modified to express the human olfactory receptor OR17-40 onto interdigitated microconductometric electrodes. This olfactory biosensor has been applied to the detection of its specific odorant (helional) with a hi...
The sections in this article are
In the framework of the SPOT-NOSED European project, nanoscale sensing elements bearing olfactory receptors and grafted onto functionalized gold substrates are used as odorant detectors. We thus develop a new concept of nanobioelectronic nose, through sensitive impedancemetric measurement of single receptor conformational change upon odorant ligand...
There is substantial interest in engineering solid supports to achieve functional immobilization of membrane receptors both for investigation of their biological function and for the development of novel biosensors. Three simple and practical strategies for immobilization of a human olfactory receptor carried by nanosomes are presented. The basis o...
In this study, we report a dose-dependent detection of odorant molecules in solution by rat olfactory receptor I7 (OR I7) in its membrane fraction. The OR I7 is immobilized on a gold electrode by multilayer bioengineering based on a mixed self-assembled monolayer and biotin/avidin system, which allows for a well-controlled immobilization of the bio...
We describe how mammalian olfactory receptors (ORs) could be used as sensing elements of highly specific and sensitive bioelectronic noses. An OR and an appropriate G a protein were co-expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells from which membrane nanosomes were prepared, and immobilized on a sensor chip. By Surface Plasmon Resonance, we were able...
We describe how mammalian olfactory receptors (ORs) could be used as sensing elements of highly specific and sensitive bioelectronic noses. An OR and an appropriate G(alpha) protein were co-expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells from which membrane nanosomes were prepared, and immobilized on a sensor chip. By Surface Plasmon Resonance, we were...
The animal olfactory system represents the gold standard of olfactory biosensors with its capability to identify and discriminate thousands of odorant compounds. In order to mimic the performances of natural olfactory sensors it is necessary to develop methods and techniques for the production, immobilization and electrical characterization of olfa...
A self‐assembled multilayer based on a mixed MHDA‐Biotinyl PE self‐assembled monolayer followed by the addition of a biotin‐avidin system was built up on the gold electrode of a quartz crystal microbalance, which was used to monitor the deposition. With the view to producing an odorant sensing device, an olfactory receptor (OR), I7 OR, was immobili...
Rhodopsin, the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) which mediates the sense of vision, was prepared from calf eyes and used as receptor enriched membrane fraction. In this study it was immobilized onto gold electrode by two different techniques: Langmuir-Blodgett (LB) and a strategy based on a self-assembled multilayer. We demonstrated that Langmuir...
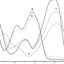
A simple impedance network model to mimic the electrical properties of a single protein molecule nanodevice is presented.
Within this model two sensing proteins of the GPCR family (bovine light-sensing rhodopsin and rat 17 olfactory receptor) in
ground and activated states are studied. We predict a detectable impedance difference between ground and...
Mention d'édition : 1st Edition
In this paper, we evaluated the grafting of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) onto functionalized surfaces, which is a primary requirement to elaborate receptor-based biosensors, or to develop novel GPCR assays. Bovine rhodopsin, a prototypical GPCR, was used in the form of receptor-enriched membrane fraction. Quantitative immobilization of the m...
Microsystems' including biomolecules is currently a research field in fast development and expansion. By coupling biomolecules to non-biological electronic transducers, molecular bioelectronic systems could one day be used in a wide variety of applications, including biosensors, biofuel cells and maybe even biocomputers. A major thrust in this fram...
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) constitute the largest but the most divergent class of cell surface proteins. Although they are thought to share a common 3D-structure composed of seven transmembrane helical domains, they can be activated by extracellular signals as diverse as light, peptides, proteins, lipids, organic odorants, taste molecules,...
The functional expression of olfactory receptors (ORs) is a primary requirement to examine the molecular mechanisms of odorant perception and coding. Functional expression of the rat I7 OR and its trafficking to the plasma membrane was achieved under optimized experimental conditions in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The membrane expre...
Primary olfactory neuronal cultures exposed to odorant stimulation have previously exhibited concentration-related effects in terms of intracellular cAMP levels and adenylate cyclase activity [Ronnett, G.V., Parfitt, D.J., Hester, L.D. & Snyder, S.H. (1991) PNAS88, 2366-2369]. Maximal stimulation occurred for intermediate concentrations, whereas AC...
The functional expression of olfactory receptors (ORs) is a primary requirement to utilize olfactory detection systems. We have taken advantage of the functional similarities between signal transduction cascades in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and mammalian cells. The yeast pheromone response pathway has been adapted to allow ligand-d...
The lutropin receptor consists of an extracellular N-terminal half and a membrane-associated C-terminal half. hCG initially binds the exodomain with a high affinity and the resulting complex is thought to interact with the endodomain through a secondary contact generating a hormonal signal. Therefore, the exodomain and endodomain are likely to asso...
Receptors for the luteotropin/human chorionogonadotropin hormone belong to the G-protein-coupled receptor family by their membrane-anchoring domains. They also possess a large extracellular domain (ECD) responsible for most of the hormone-receptor interactions. Structure-function studies identified several contacts between hormone and receptor ECD,...
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) via interaction with G-protein coupled specific receptors plays a central role in the control of gametogenesis in mammals of both sexes. In females, FSH is crucial for follicle growth, follicle maturation and ovulation. FSH receptors, together with luteinizing hormone-chorionic gonadotropin and thyrotropin recepto...
The lutropin receptor ectodomain overexpressed under the control of the powerful polyhedrin promoter in baculovirus‐infected Sf9 insect cells, is mainly found in an inactive, intracellularly‐aggregated form. It is secreted in an active form under the control of the P10 promoter, a somewhat weaker and earlier promoter, at the price of a lower produc...
In porcine Leydig cells in primary culture, 95% of the internalization of [125I]porcine lutropin ([125I]pLH, which bears sulfated GalNAc) could not be ascribed to the high-affinity LH receptor (LHR). In contrast, >40% of [125I]human choriogonadotropin (hCG, with sialylated sugar chains) uptake was performed by the LHR itself. When the LHR was down-...
Large-scale synthesis of active recombinant porcine luteinizing hormone/chorionic gonadotropin receptor (pLHR) is required for biophysical and structural studies. This study was undertaken to improve expression of the corresponding cDNA already obtained with a number of other systems, (i) by turning to cells from mammalian origin able to perform ad...
Molecular forms of the porcine LH/CG receptor (pLHR) and complexes between hCG and either the full-length pLHR or its extracellular domain (ectodomain) have been produced in various recombinant systems. In COS cells and in the baculovirus insect cells system, the co-expression of the ecto- and endo-domains reconstituted a functional receptor where...
The monoclonal antibody, HT13 recognizes human choriogonadotropin (CG) bound to the extracellular domain of its receptor, but not to the full-length receptor. The HT13 epitope is located in the regions of residues 15-17 and 73-75 of the human CG alpha-subunit. Only one synthetic peptide, lutropin (LH)/CG-receptor-(481-497)-peptide (EL2 peptide), wh...
The LH/hCG receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor with an N-terminal extracellular domain involved in hormone—receptor interaction. The recombinant porcine receptor, stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, has the same characteristics ( K d and cAMP production) as in Leydig cells. Six synthetic peptides derived from the receptor ec...
The porcine follitropin receptor-encoding cDNA (pFSHR) was cloned using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Total RNA from porcine granulosa cells was used as template. Two overlapping cDNA fragments encoding, respectively, as 1 to 290 and as 191 to 694 of the pFSHR were obtained. Taken together, the two fragments represented...
Overexpression of the porcine LH receptor (pLHR) ectodomain has been achieved using the baculovirusinsect cell system but mostly in an aggregated form with no secretion. In order to carry this out, new baculoviruses were selected to produce the pLHR ectodomain in insect Sf9 cells and caterpillars. In pLHR-P10–297 and pLHR-mel-319 baculoviruses, pLH...
Porcine LH receptor ectodomain was overexpressed in insect cells and lepidopteran larvae using the recombinant baculovirus expression system. A low multiplicity of infection yielded the largest active production, of approximately 10(7) receptors/cell or 3 micrograms active receptor/mg total protein in infected cells. The truncated ectodomain solubi...
Cryopreservation procedures of living cells involve the use of organic solvents against freezing damage. An efficient cryoprotection might be achieved by obtaining a cytoplasmic gel able to reduce water flux and avoid crystallization. Small angle X-ray scattering experiments were performed at LURE (Orsay, France) to investigate the effects of 1.2-p...
Organic cryosolvents essential for cryopreservation of living cells have a colligative effect on water properties, but also affect cellular structures such as the membrane, actin, or tubulin cytoskeleton. The effects of cryosolvents on actin and its binding proteins are starting to be well investigated. In parallel, tubulin assembly characteristics...
In previous studies, we demonstrated that 1,2-propanediol induces shortening and bundling of actin filaments, both in vitro and in vivo, and that it enhances actin/alpha-actinin interaction, especially at low temperature. 1,2-Propanediol also promotes homogeneous microporous networks which can be vitrified by rapid cooling. In the present study, dy...
Small-angle X-ray scattering was used to probe the structure of actin in the presence of cryosolvents: 1,2-propanediol, glycerol, or a mixture of both solvents. In media devoid of polymerizing salts, a radius of gyration of 23 A is measured, as expected from the literature. In the presence of 1,2-propanediol alone, the scattering pattern begins to...
Water flux and crystallization are major problems for cryopreservation. The gel approach relies on the concept that a biological gel network might sufficiently entrap fluid within its pores, so as to maintain its osmotically inactive under the stresses usually encountered in the course of cryopreservation and limit the extent of crystallization. It...
A dynamic equilibrium between globular and filamentous actin plays a crucial role in cell structure and motility. Many factors such as pH, ionic strength, temperature, and divalent cations, are known to influence this equilibrium. Some organic solvents, such as those used for the cryopreservation of cells, may also alter the dynamic equilibrium of...
Freezing tolerance and resistance in nature are among the most important and challenging aspects of biochemical adaptation to extreme environments. Some biochemical strategies are known but their mechanism is still poorly understood. Cryopreservation of cells and tissues of sensitive organisms is still generally based on physical chemistry rather t...
The influence of 1,2-propanediol on the G-actin/F-actin equilibrium has been studied previously. We report here its effect on the crosslinking of actin filaments by alpha-actinin. Capillary viscometry experiments indicate a marked increase in the viscosity of F-actin/alpha-actinin solutions in the presence of this solvent, with a rise of the gel po...
Commonly used cryopreservation procedures are empirical and involve incompletely understood phenomena. Our purpose is to study in vitro the cryobehavior of a number of biopolymers participating in cell structure or its environment. Their abilities to interact with water to obtain gelified structures might be a good means to reduce the water mobilit...
A conformational analysis of meso and racemic 1,1′-di (2-naphthyl)-diethylether has been performed using the semiempirical differential PCILO method. The most stable ground-state and excimer conformations were determined as well as the potential barriers involved in intramolecular excimer formation. The results of the calculations were compared wit...








![Fig. 4 AFM image of sonicated nanosomes on bare gold (coverage 50%) [6]](profile/Yanxia-Hou-3/publication/332668491/figure/fig5/AS:784820347084801@1564127160336/AFM-image-of-sonicated-nanosomes-on-bare-gold-coverage-50-6_Q320.jpg)























































































![Figure 10 : Modelization of single receptor electrical behavior [11]....](profile/Edith-Pajot-Augy/publication/4306341/figure/fig3/AS:527952905736192@1502885189566/Modelization-of-single-receptor-electrical-behavior-11-A-Rhodopsin-fundamental-and_Q320.jpg)















































