Fig 2 - uploaded by Raúl J. Martín-Palma
Content may be subject to copyright.
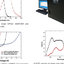
Values of the optical constants in the visible wavelength range corresponding to the glass substrate.
Source publication
In the present work a formalism is developed based on the matrix
method for the purpose of obtaining the values of the optical constants
(n refractive index and k extinction coefficient) of thin film materials
from the experimental reflectance (R) and transmittance (T) spectra.
This formalism has been applied to the determination of the dependence...
Context in source publication
Context 1
... HYBRD1, which uses a modification of Powell's hybrid algorithm [12], [13]. The numerical method of inversion stops when the accuracy of the results is better than 10 . It can be noted the high degree of precision in the simulation of these spectra which allows to determine the values of the op- tical constants with a high degree of accuracy. Fig. 2 shows the values of the refractive index and the extinction coefficient of the bare glass substrate obtained from the simulated and spectra, which are necessary to be lately employed in the deter- mination of the values of the optical constants corresponding to the SnO film. From these values it can be observed that those corresponding ...
Similar publications
Haze is a phenomenon which occurs when there is a great amount of tiny particulates suspended in the atmosphere. During the period of March 2014, a long period of haze event occurred in Penang, Malaysia. The haze condition was measured and monitored using a ground-based Lidar system. By using the measurements obtained, we evaluated the performance...
Acceptor end-capping of oligomeric conjugated molecules is found to be an effective strategy for simultaneous spectra broadening, extinction coefficient enhancement, and energy level optimization, resulting in profoundly enhanced power conversion efficiencies (of 9.25% and 8.91%) compared to the original oligomers. This strategy is effective in ove...
Phytoplankton and zooplankton were sampled in Chennai and Parangipettai coast, south-western part of Bay of
Bengal (BoB) at monthly scale from August 2013 to July 2014. Physico-chemical parameters such as sea surface temperature (SST), pH, salinity, Dissolved Oxygen (DO), Total Suspended Solids (TSS), Light Extinction Coefficient (LEC), nitrate, am...
An existing two-layer model for forest height estimation is adapted for agricultural crops in order to develop a retrieval algorithm based on polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interferometry. This new inversion scheme is specifically tailored for vertically oriented agricultural crops, with extinction coefficients dependent on the wave polariza...
Citations
... The software is based Silicon on spectral reflectance and transmittance data. In this case, the materials under study is described as a plane-parallel layer of infinite extent, characterized by an index of refraction n and an extinction coefficient k [14,15]. In the general case of a multilayer coating, each interface and homogeneous layer would be described by its appropriate matrix. ...
The precise knowledge of the values of the optical constants (index of refraction, n, and extinction coefficient, k) for nanostructured porous silicon (nanoPS) is a necessary condition to predict the behavior of any optical and photonic devices based on this material. With this objective in mind, a simulation computational program based on the matrix method was used to determine the values of the optical constants in the visible range of self-standing nanoPS films from their experimental reflectance and transmittance spectra. Furthermore, the spectral absorption coefficient (α) was determined from the spectral k values, which motivated to the determination of the values and type of bandgap (direct or indirect) for different porosities.
... The software is based on spectral re ectance and transmittance data. In this case, the materials under study is described as a plane-parallel layer of in nite extent, characterized by an index of refraction n and an extinction coe cient k [14]. Accordingly, each interface and homogeneous layer in a multilayer coating is described by its appropriate matrix. ...
The precise knowledge of the values of the optical constants (index of refraction, n , and extinction coefficient, k ) for nanostructured porous silicon (nanoPS) is a necessary condition to predict the behavior of any optical and photonic devices based on this material. With this objective in mind, a simulation computational program based on the matrix method was used to determine the values of the optical constants in the visible range of self-standing nanoPS films from their experimental reflectance and transmittance spectra. Furthermore, the spectral absorption coefficient ( α ) was determined from the spectral k values, which motivated to the determination of the values and type of bandgap (direct or indirect) for different porosities
... As the first step of the process, we determine the complex refractive indices of the solution-processed materials. For this purpose, we apply the reflectance-transmittance method that does not require any pre-defined dispersion function models [12,13]. Then, by means of experimental techniques as well as advanced optical simulations using the optical simulator CROWM (Combined Ray Optics / Wave Optics Model) [14,15], detailed optical analysis of standalone micro-textured light management foil as well as the complete organic solar cell is performed. ...
... Its accurate acquisition is therefore of great importance for reliable simulations. In the case of organic solution-processed materials, we found out that the reflectance-transmittance (RT) method [12] is especially suitable. It is simple, fast, can be applied to thin and thick layers, and delivers results directly without the need for fitting to the (often unknown) dispersion models (e.g. as is the case in ellipsometry [24]). ...
We present detailed numerical and experimental investigation of thin-film organic solar cells with a micro-textured light management foil applied on top of the front glass substrate. We first demonstrate that measurements of small-area laboratory solar cells are susceptible to a significant amount of optical losses that could lead to false interpretation of the measurement results. Using the combined optical model CROWM calibrated with realistic optical properties of organic films and other layers, we identify the origins of these losses and quantify the extent of their influence. Further on, we identify the most important light management mechanisms of the micro-textured foil, among which the prevention of light escaping at the front side of the cell is revealed as the dominant one. Detailed three-dimensional simulations show that the light-management foil applied on top of a large-area organic solar cell can reduce the total reflection losses by nearly 60% and improve the short-circuit current density by almost 20%. Finally, by assuming realistic open-circuit voltage and especially the realistic fill factor that deteriorates as the absorber layer thickness is increased, we determine the optimal absorber layer thickness that would result in the highest power conversion efficiency of the investigated organic solar cells.
... This approach is applicable if we know the reflectance coefficient r b of the entire stack of layers after each incoherent layer. In case of flat interfaces this can be pre-calculated analytically, e.g., using transfer matrix method [20]. Due to simplicity reasons we are showing the model for 2-D domain with the propagation in xy-direction. ...
In multidimensional numerical simulations of optoelec-tronic devices the rigorous Maxwell equations are solved in different ways. However, numerically efficient incoherent propagation of light inside the layers has not been resolved yet. In this paper we present two time-and resource-efficient approaches for optical simulations of incoherent layers embedded in multilayer structures: (a) phase match-ing and (b) phase elimination approach. The approaches for simulat-ing the incoherent propagation of light in thick layers are derived from Maxwell equations. Both approaches can be applied to any layer in the structure regardless of the position inside the structure and the number of incoherent layers. In rigorous simulations, for low absorbing thick layers scaling down the thickness and increasing extinction coefficient of the layer proportionally is implemented to shorten computational time. The simulation results are verified with the experiment on two types of structures: a bare glass incoherent layer and an amorphous silicon solar cell.
... The Transfer Matrix Method (TMM) applied in (Hugon, Benech & Gagnaire 1998) 14 and described in (Chen et al. 2000;Chilwell & Hodgkinson 1984;Martin-Palma, Martinez-Duart & Macleod 2000;Walpita 1985), is today one of the primary tools used for the analysis of multilayer optical waveguides of a variety of waveguide combinations of lossless or lossy materials such as metals and dielectrics, generating TE and TM mode dispersion equations that yield the modal propagation constants and EM field distributions for each. ...
... The transfer matrix (TM) method has been widely used to determine the values of the optical constants and thickness of thin films from their reflectance spectra in the visible wavelength range [1][2][3][4][5]. The photon transport through the multilayered structure is usually described using the TM method. ...
The reflectivity spectra have been traditionally used to determine the thicknesses in semiconductor films. However, thicknesses of nanofilms are not easy to evaluate because the interference fringes are not visible in the transparent region. In this paper, we present a computed method based on the transfer matrix (TM) which is used to match the calculated and experimental room temperature reflectivity spectra of the ZnTe/GaAs films and to determine its thickness film values afterwards. The TM method needs only to know refraction indices and absorption coefficients as a function of wavelength for the film and the substrate. The thickness nanofilms evaluated by our method are in agreement with the values measured by ellipsometry, Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy techniques. The present procedure extends the application of the standard spectral reflectance technique to determine semiconductor nanolayer thicknesses.
We propose a teaching apparatus to simultaneously measure the refractive index and thickness of a thin film. The apparatus includes: a diode laser, a polarizer, a spectrometer, a photodiode and a portable digital multimeter. With the apparatus, we measure the refractive index and thickness of two thin films (a silicon dioxide film on silicon, a silicon nitride film on silicon). The maximum discrepancy between our apparatus and an ellipsometer is 1.4%. We also analyze the errors of our apparatus by numerical simulations. The lab with the apparatus described here has several valuable pedagogical outcomes: 1) understanding the multi-beam interference in a film; 2) applying chi-square minimization; 3) carrying out the nonlinear curve fitting with multiple parameters. The lab can be used in an optical polarization teaching for undergraduate sophomores.
On 29 April 2021, Professor Hugh Angus Macleod, Angus as he was known to his family and friends, passed away at his home in Tucson, Arizona. Angus was a leading authority in the field of thin film optics, and he leaves behind a legacy of extraordinary contributions to the thin film community. This article outlines Angus’s career in optics—a career that spanned over 60 years. Not only was Angus an eminent and distinguished scientist, he was also a great teacher, mentor, colleague and friend to the entire thin film optics world.
An optical model for simulation of thin-film photovoltaic devices with thick surface-textured front components is presented. The model is based on the combination of incoherent geometric optics and coherent wave optics analysis, which are employed separately to simulate light propagation through the front textured component and the bottom flat thin-film component of the device, respectively. The verified model is implemented into the optical simulator CROWM, which is employed to study the light-trapping potential of the front surface-textured protective glass in thin-film photovoltaic modules. The results show that the texturisation in the range of millimetres significantly improves the quantum efficiency of the PV module, which results in 14.3% higher J(SC) compared to the conventional module with flat protective glass.