Figure - available from: Medicinal Chemistry Research
This content is subject to copyright. Terms and conditions apply.
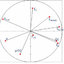
The scatter plot of macrocyclic ring size vs. pIC50 activity values. Circle indicates compounds having four H-bonds; square indicates compounds having three H-bonds and triangle indicates compounds having two H-bonds
Source publication
Macrocyclic ring structures could have drug-like properties such as membrane permeability, metabolic stability, binding affinity, selectivity, and high-biological activities. Synthesized macrocyclic inhibitors have been studied and the effect of ring size has gained attention from drug design community. Marsault et al. showed a positive correlation...
Similar publications
QSAR models of 25 iminoguanidine derivatives with inhibitory HemO were developed. The QSAR model was built by using DFT-MLR and the best QSAR model has R 2 , Q 2 values of 0.6569 and 0.5493 for cross-validated and non-cross-validated. The predictive ability of QSAR model was further validated by a test set of 7 compounds, giving R 2 pred value of 0...
The computational proficiencies put on in this screening are QSAR, with fraction of variance r2 = 0.8499 and LOO-CV q2 = 0.5008. 3D-QSAR (CoMFA and CoMSIA) and structure-based approach (molecular dynamics simulations assisted molecular docking study) were applied for the identification of important features of iminoguanidine-based, responsible for...
A series of twenty one thiadiazole-thiazolone derivatives which is a class of highly potent human mitotic kinesin Eg5 inhibitor reported from published article were studied through a series of computer-aided drug design processes such as three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR) modeling, including comparative molecul...
The 3D-QSAR models were established in this study based on comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity index analysis (CoMSIA), the optimal CoMFA model established gave \({\text{Q}}^{2}\)= 0.671, \({\text{R}}^{2}\)= 0.925 and \({\text{R}}_{\text{p}\text{r}\text{e}\text{d} }^{2}\)= 0.868, and the best CoMSIA/SEA...
Citations
... Extensive SAR (structureactivity relationship) investigations revealed that analog 8, also known as UNC2541, emerged as a crucial compound with remarkable sub-micromolar inhibitory potency. Additionally, an X-ray structure of MerTK in complex with compound 8 ((S)-7-amino-N-(4-fluorobenzyl)-8-oxo-2,9,16-triaza-1(2,4)-pyrimidinacyclohexadecaphane-1 5 -carboxamide) was resolved to show that these macrocycles bind in the MerTK ATP pocket (PDB ID: 5K0X) [10]. ...
Kinases play an important role in regulating various intracellular signaling pathways that control cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, and other cellular processes, and their deregulation causes more than 400 diseases. Consequently, macrocyclization can be considered a noteworthy approach to developing new therapeutic agents for human diseases. Macrocyclization has emerged as an effective drug discovery strategy over the past decade to improve target selectivity and potency of small molecules. Small compounds with linear structures upon macrocyclization can lead to changes in their physicochemical and biological properties by firmly reducing conformational flexibility. A number of distinct protein kinases exhibit similar binding sites. Comparison of protein binding sites provides crucial insights for drug discovery and development. Binding site similarities are helpful in understanding polypharmacology, identifying potential off-targets, and repurposing known drugs. In this review, we focused on comparing the binding sites of those kinases for which macrocyclic inhibitors are available/studied so far. Furthermore, we calculated the volume of the binding site pocket for each targeted kinase and then compared it with the binding site pocket of the kinase for which only acyclic inhibitors were designed to date. Our review and analysis of several explored kinases might be useful in targeting new protein kinases for macrocyclic drug discovery.
... Besides, artificial inhibitors with large ring structures were synthesized and examined for inhibitory activity against several targets. Various studies about ring size effects over the potency of inhibitors were reported earlier [10]. Marsault and Peterson (2011) reported that macrocyclic inhibitors of renin showed rise in inhibitory activity with increase in ring size (from 10-to 14-membered rings) [11]. ...
... Nevertheless, additional increase in the ring size resulted in a significant reduction of the potency [12,13]. Moreover, naturally occurring macrocyclic compounds have the ring sizes that span from 11-to 16-membered rings, most frequently 14 membered (Madsen and Clausen 2011) [10]. Hence, the effect of ring size is very intriguing, which can be applicable to study the interactions obtained by macrocyclic inhibitors with their target [10,12,13]. ...
... Moreover, naturally occurring macrocyclic compounds have the ring sizes that span from 11-to 16-membered rings, most frequently 14 membered (Madsen and Clausen 2011) [10]. Hence, the effect of ring size is very intriguing, which can be applicable to study the interactions obtained by macrocyclic inhibitors with their target [10,12,13]. Some of the naturally occurring macrocyclic compounds are erythromycin (antibiotic), epothilone B (anticancer), tacrolimus (immunosuppressant), and bryostatins (protein kinase C inhibitor) [10]. ...
Kinases play an important role in regulating various intracellular signaling pathways that control cell proliferation, differentiation, survival and other cellular processes and their deregulation causes more than 400 diseases. Consequently, macrocyclization can be considered a noteworthy approach to develop new therapeutic agents for human diseases. Macrocyclization has emerged as an effective drug discovery strategy over the past decade to improve target selectivity and potency of small molecules. Small compounds with linear structures upon macrocyclization can lead to changes in their physicochemical and biological properties by firmly reducing conformational flexibility. A number of distinct protein kinases exhibit similar binding sites. Comparison of protein binding site provides crucial insights for the drug discovery and development. Binding site similarities are helpful to understand polypharmacology, identifying potential off-targets and repurposing of known drugs. In this review, we focused on comparing binding sites of those kinases for which macrocyclic inhibitors are available/studied so far. Furthermore, we calculated the volume of binding site pocket for each targeted kinase and then compared it with the binding site pocket of the kinase for which only acyclic inhibitors were designed till date. Our review and analysis of several explored kinases might be useful to target new protein kinases for macrocyclic drug discovery.
... Another crucial receptor involved in melanoma progression and development is MERTK. It is a member of the family of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) which have been characterized as a therapeutic target in hematopoietic malignancies and various tumors such as melanoma, lung, prostate, and brain tumors [7,8]. The Mer receptor tyrosine kinase is a cell surface receptor that mediates phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and modulates cytokine production, and is found on macrophages. ...
Recent studies have revealed that MERTK and BRAF V600E receptors have been found to be over-expressed in several types of cancers including melanoma, making these receptors targets for drug design. In this study, we have designed novel peptide conjugates with the natural products vanillic acid, thiazole-2-carboxylic acid, cinnamic acid, theanine, and protocatechuic acid. Each of these compounds was conjugated with the tumor targeting peptide sequence TAASGVRSMH, known to bind to NG2 and target tumor neovasculature. We examined their binding affinities and stability with MERTK and BRAF V600E receptors using molecular docking and molecular dynamics studies. Compared to the neat compounds, the peptide conjugates displayed higher binding affinity toward both receptors. In the case of MERTK, the most stable complexes were formed with di-theaninate-peptide, vanillate-peptide, and thiazole-2-amido peptide conjugates and binding occurred in the hinge region. Additionally, it was discovered that the peptide alone also had high binding ability and stability with the MERTK receptor. In the case of BRAF V600E, the peptide conjugates of protocatechuate, vanillate and thiazole-2-amido peptide conjugates showed the formation of the most stable complexes and binding occurred in the ATP binding cleft. Further analysis revealed that the number of hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions played a critical role in enhanced stability of the complexes. Docking studies also revealed that binding affinities for NG2 were similar to MERTK and higher for BRAF V600E. MMGBSA studies of the trajectories revealed that the protocatechuate–peptide conjugate showed the highest binding energy with BRAF V600E while the peptide-TAASGVRSMH showed the highest binding energy with MERTK. ADME studies revealed that each of the compounds showed medium to high permeability toward MDCK cells and were not hERG blockers. Furthermore, the conjugates were not CYP inhibitors or substrates, but they were found to be Pgp substrates. Our results indicated that the protocatechuate-TAASGVRSMH, thiazole-2-amido-TAASGVRSMH, and vanillate-TAASGVRSMH conjugates may be furthered developed for in vitro and in vivo studies as novel tumor targeting compounds for tumor cells over-expressing BRAF V600E, while di-theaninate-amido-TAASGVRSMH and thiazole-2-amido-TAASGVRSMH conjugates may be developed for targeting MERTK receptors. These studies provide insight into the molecular interactions of natural product-peptide conjugates and their potential for binding to and targeting MERTK and BRAF V600E receptors in developing new therapeutics for targeting cancer.
Graphical abstract
... The number of grid points in x, y, and z direction was set to 60, 60, and 60 with a spacing value of 0.375 Å. The Lamarckian genetic algorithm was used for ligand conformational search; the parameters were set the same in the previous studies (Lu et al. 2014;Bhujbal et al. 2019;Sciú et al. 2019). During docking, the protein CDK2 was treated as rigid, and the inhibitor PF-367 was treated as flexible molecule. ...
Kinase inhibitor selectivity is a major concern for the design of small-molecule compounds. As a member of serine/threonine protein kinase family, glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) is involved in diverse biological processes and abnormal dysregulation of its activity has been associated with several pathologies, including type II diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, bipolar disorders, and cancers. A small-molecule PF-367 significantly inhibited the GSK3 enzymatic activity over its closest cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) with >1000-fold selectivity. However, the PF-367 selectively binding to GSK3β over CDK2 has remained unclear. Here, molecular docking, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, and molecular mechanics_generalized born/surface area (MM_GBSA) binding free energy calculations, as well as the decomposition of binding free energies were performed to investigate the selective binding mechanism of PF-367 to the ATP-binding site of GSK3β over CDK2. The results revealed that the exposure of the terminal triazole ring of PF-367 into the solvent environment may be responsible for the weak binding complex of CDK2−PF-367, which was further confirmed by the binding free energy calculations and the identified key residues (Phe67, Lys85, Thr138, and Arg141) contributing to the binding interaction. The obtained data can not only decipher the origin of selectivity, but also be used for the design of more potent and selective GSK3β inhibitors.