Figure 4 - uploaded by Ivan Bristow
Content may be subject to copyright.
Source publication
Malignant melanoma is a life threatening skin tumour which may arise on the foot. The prognosis for the condition is good when lesions are diagnosed and treated early. However, lesions arising on the soles and within the nail unit can be difficult to recognise leading to delays in diagnosis. These guidelines have been drafted to alert health care p...
Context in source publication
Context 1
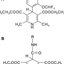
... subungual bleed will normally have arisen within a day or two and may be associated with an epi- sode of trauma, or more commonly, a period of vigor- ous activity or sport where no trauma is recollected. Having been noted, it will not change greatly, although the clinician will note a distal drift with time if they review over a period of several months [30] (Figure 4). ...
Citations
... [23,24] Practical biopsy is important for diagnosis. [25] ...
The purpose of the study is to analyse and to identify specific structural characteristics of melanocytic nevi. So, for better conclusions, using the optical microscope, could be possible a proper describtion related melanocytic nevi, reffering to youth pacients. In this research direction, good to mention that in a human individual life, play a significant role, different factors. That include in line, genetic, epigenetic, microbiomic, and proteomic factors. Future directions refers to preventive and prophylactic methods.
... The differential diagnosis for SUM includes subungual hematoma, subungual hemorrhage, paronychia, pyogenic granuloma, onychomycosis, warts, callus, glomus tumor, benign nevus, poroma, subungual fibroma, keratoacanthoma, Bowen's disease, and subungual squamous cell carcinoma. 2,10,11 The case presented here highlights the importance of a prompt biopsy of clinically suspicious lesions due to the quick and aggressive nature of melanoma. ...
... The acronym "CUBED" can be used as an alternative acronym to highlight potential melanoma on the foot (Table 1(a)). 11 Another framework that can be used to clinically assess and identify features of early malignant melanomas on nail examination is the "ABCDEF" criteria proposed by Levit et al. 15 (Table 1(b)). ...
Subungual melanoma is a rarer form of melanoma encountered in clinical practice that often has a poor prognosis because it presents with advanced disease. We report a case of a 46-year-old male with a circumferential osteoinvasive melanoma that invaded the superior and lateral aspects of the periosteum of the distal phalanx. We discuss pathologic findings and common physical exam findings to facilitate earlier diagnosis of subungual melanoma.
... Although the efficacy of CUBED in distinguishing benign lesions from ALM has not been assessed, established referral networks between local providers, such as podiatrists, and dermatologists may facilitate timely diagnosis and management of ALM. 6,7 Acquired Acral Melanocytic Nevi ...
Background:
Survival outcomes in acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) are worse than for cutaneous melanoma. Diagnostic delays are believed to contribute to worse outcomes in ALM, including advanced-stage disease at initial presentation. Acral lentiginous melanoma, especially in its early stages, may be difficult to discern from benign pigmented acral lesions.
Objective:
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive review of the diagnosis and management of acral pigmented lesions.
Materials and methods:
A literature review was performed. The outcomes included were the clinical and dermoscopic features and the management frameworks and considerations for acquired and congenital melanocytic nevi, acral melanosis, nonmelanocytic pigmented lesions, and ALM.
Results:
Original research studies were primarily included. The use of dermoscopy, such as the 3-step algorithm and blotch (irregular), ridge pattern (parallel), asymmetry of structures, asymmetry of colors, furrow pattern (parallel), fibrillar pattern (BRAAFF) checklist, increases the diagnostic accuracy of acral pigmented lesions with high specificity and sensitivity. Short-term digital dermoscopic surveillance can be used to manage acral lesions, and histopathology should be collected when there is a concern for ALM.
Conclusion:
The use of dermoscopy and an understanding of how to manage acral lesions may limit the number of biopsies performed on the acral skin, decrease the time to diagnosis, and facilitate early detection of ALM.
... The prognosis depends on the histological thickness of the excised tumor (Breslow depth) and tends to be poor in patients with AM. Several studies based on a large number of case series demonstrate a significant rate of mortality and tumor recurrences, as well as lower melanoma-specific survival (MSS), melanoma-free survival (MFS), 5year survival, and overall survival (OS) [12,16]. ...
Introduction and importance: Amelanotic melanoma is a rare and aggressive type of melanoma. It is often diagnosed late because of the lack of melanin in its cells, and this causes treatment delay and, eventually, poor prognosis.
Case presentation: We report a case of a 79-year-old female patient that presented to the dermatology clinic with an asymptomatic lesion on the medial heel of the right foot, with no medical history of previous melanoma or related skin cancer. To get the right diagnosis, an incisional biopsy was performed, and the sample was sent to the pathology laboratory. The sample was stained with S100 and HMB-45 stains, and both were positive. Also, no melanin pigmented cells were seen, so the diagnosis was amelanotic nodular melanoma. The patient was then referred to surgery. The lesion was successfully excised with 5cm safety margins, and the whole lesion was sent to
the pathology laboratory to ensure that the edges are malignancy-free. After 18 months of follow-up, the patient is in good health.
Conclusion: Accurate and early diagnosis with appropriate clinical intervention can improve the prognosis and
reduce mortality and morbidity rates.
... Most of the currently available clinical therapies have been developed for major melanoma subtypes, such as SSM, which often occurs in the UV-exposed skin, and there are very few effective treatments for minor subtypes such as ALM, which often occurs on the plantar surface [12,13]. For instance, the molecular targeted drugs and immune checkpoint inhibitors that target mutation, such as BRAF and NRAS gene, are effective for SSM, but ALM has a poor response to these treatments because there are relatively few above-mentioned genetic mutations [14][15][16][17]. Therefore, the development of effective treatment and diagnostic strategy for minor melanoma subtypes, such as ALM, is also vitally important. ...
... Pathological diagnosis of minor melanoma subtype, which often occurs on the soles of feet, is difficult compared to other melanoma types [6][7][8]. In addition, the minor subtype responds poorly to current therapy strategies [14][15][16]. For these reasons, it is important to elucidate the mechanisms by which these minor melanoma progress to establish new pathological diagnostic strategies and therapies. ...
Static mechanical compression is a biomechanical factor that affects the progression of melanoma cells. However, little is known about how dynamic mechanical compression affects the progression of melanoma cells. In the present study, we show that mechanical intermittent compression affects the progression rate of malignant melanoma cells in a cycle period-dependent manner. Our results suggest that intermittent compression with a cycle of 2 h on/2 h off could suppress the progression rate of melanoma cells by suppressing the elongation of F-actin filaments and mRNA expression levels related to collagen degradation. In contrast, intermittent compression with a cycle of 4 h on/4 h off could promote the progression rate of melanoma cells by promoting cell proliferation and mRNA expression levels related to collagen degradation. Mechanical intermittent compression could therefore affect the progression rate of malignant melanoma cells in a cycle period-dependent manner. Our results contribute to a deeper understanding of the physiological responses of melanoma cells to dynamic mechanical compression.
... Delays in diagnosis of amelanotic acral lesions, particularly involving the nail unit, is a frequent issue secondary to inconsistent features of early melanoma potentially leading to diagnosis in later stages of development. Two main patterns of subungual melanoma have been described: longitudinal melanonychia and amelanotic tumors [11]. Longitudinal melanonychia originates from the nail matrix, while nonpigmented subungual nodules usually coupled with onycholysis typically originate from the nail bed [12]. ...
... This anatomical relationship might encourage surgeons to opt for amputation as opposed to less aggressive surgical management [16]. Bristow et al. [11] suggest a specialist referral and surgical removal for histologic purposes when presented with a pyogenic granuloma, granulomatous masses, lesions that do not respond within 2 months, and any lesions that disturb the integrity of the nail. A heightened index of suspicion is necessary in any nonhealing and suspiciouslooking lesion. ...
Introduction:
Amelanotic melanoma is a rare subtype, which may be clinically difficult to diagnose due to lack of pigmentation and variable histopathological features. Osteoinvasion is another rare characteristic of melanoma. There are few reports in the literature of amelanotic melanoma of the nail unit (nail bed, matrix, and nail folds) with invasion of bone.
Case presentation:
We present a case of a 73-year-old Caucasian male with a 13-month history of an ungual lesion on his right hallux. The lesion was initially treated as a chronic diabetic ulceration with failure to resolve with standard of care.
Discussion/conclusion:
A heightened index of suspicion for a malignant process is necessary when standard of care fails to lead to improvement or resolution. In these instances, biopsy should be seriously considered.
... Cutaneous melanomas are curable when diagnosed in the earlier stage (~98% survival rate) but once metastasised, they are tough to cure (~25% survival rate); thus, early identification of melanoma has been deemed crucial for the patient's survival [7,8]. This uncertainty between patient's death or survival is directly affected by the choice of the therapy given to the patients, which in turn depends on the features that were used for prognostication. ...
... These genes mainly encode for proteins that are directly related to promoting cell death and are under-expressed in tumor cells. Examples include MCL1, XIAP, FAS, FASLG, Caspases [3,7,8], which are key players in the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathway [66,67]. The PI for these 29 genes was able to significantly discriminate between high and low-risk patients by a 2.5 hazard ratio. ...
... Cutaneous melanomas are curable when diagnosed in the earlier stage (~98% survival rate) but once metastasised, they are tough to cure (~25% survival rate); thus, early identification of melanoma has been deemed crucial for the patient's survival [7,8]. This uncertainty between patient's death or survival is directly affected by the choice of the therapy given to the patients, which in turn depends on the features that were used for prognostication. ...
... These genes mainly encode for proteins that are directly related to promoting cell death and are under-expressed in tumor cells. Examples include MCL1, XIAP, FAS, FASLG, Caspases [3,7,8], which are key players in the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathway [66,67]. The PI for these 29 genes was able to significantly discriminate between high and low-risk patients by a 2.5 hazard ratio. ...
Risk assessment in cutaneous melanoma (CM) patients is one of the major challenges in the effective treatment of CM patients. Traditionally, clinico-pathological features such as Breslow thickness, American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) tumor staging, etc. are utilized for this purpose. However, due to advancements in technology, most of the upcoming risk prediction methods are gene-expression profile (GEP) based. In this study, we have tried to develop new GEP and clinico-pathological features-based biomarkers and assessed their prognostic strength in contrast to existing prognostic methods. We developed risk prediction models using the expression of the genes associated with different cancer-related pathways and got a maximum hazard ratio (HR) of 2.52 with p-value~1e-8 for the apoptotic pathway. Another model, based on combination of apoptotic and notch pathway genes boosted the HR to 2.57. Next, we developed models based on individual clinical features and got a maximum HR of 2.45 with p-value~1e-6 for Breslow thickness. We also developed models using the best features of clinical as well as gene-expression data and obtained a maximum HR of 3.19 with p-value~1e-9. Finally, we developed a new ensemble method using clinical variables only and got a maximum HR of 6.40 with p-value 1e-15. Based on this method, a web-based service and an android application named 'CMcrpred' is available at (https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/cmcrpred/) and Google Play Store respectively to facilitate scientific community. This study reveals that our new ensemble method based on only clinico-pathological features overperforms methods based on GEP based profiles as well as currently used AJCC staging. It also highlights the need to explore the full potential of clinical variables for prognostication of cancer patients.
... Mycological examination allowed a diagnosis of onychomycosis in 8 (18%) nails. Considering the prevalence of onychomycosis in the population, it can be suggested that nails with onychomycosis have a greater tendency to trauma resulting in hematoma than normal nails [14][15][16]. It is obvious that in order to confirm this proposal, more studies involving a larger sample size are needed. ...
Introduction:
There are very few studies focusing on the dermoscopic features of subungual hematoma which is one of the major imitators of subungual melanoma.
Aim:
To identify the dermoscopic findings of subungual hematoma, which will facilitate the diagnostic process by reducing the use of more invasive diagnostic methods like nail avulsion or biopsy.
Material and methods:
In this study, clinical and dermoscopic findings of the cases were reviewed. The diagnosis of subungual hematoma was confirmed by observing progression of the colour change to the distal edge of the nail plate in all the cases.
Results:
A total of 47 subungual hematomas were enrolled in the study. The most common colour was purple-black (53%). Blue-white colour was observed in 12 (26%) lesions. 9 (19%) lesions showed granular leukonychia. All of the lesions had a homogenous pattern. In 25 (53%) lesions, a globular pattern was observed. 14 (30%) lesions showed a streaks pattern. Peripheral fading and periungual haemorrhage were present in 14 (30%) and 9 (9%) lesions, respectively.
Conclusions:
We detected two new findings which have not been described previously for subungual hematoma: the first one is "blue-white colour" which is known as an important clue to melanoma. The second one is granular leukonychia localized on the hematoma. We suggest that in any case of the nail discoloration, a thorough dermoscopic examination should be performed. Moreover, progression of the colour change to the distal edge should be observed to ensure that a possible melanoma is not overlooked.
... The disease may be confusing, leading to misdiagnosis of the lesion. 7,8 As with any type of malignant melanoma, the most important survival indicators are tumour thickness, ulceration and lymph node metastases. Because of infrequent checks of the acral skin, the lesion is often diagnosed quite late with big tumour thickness. ...
Melanoma is an aggressive skin cancer form with a grave prognosis. Current results suggest that oncolytic virus treatment of melanoma has a high therapeutic potential. ECHO-7 (Rigvir) is the first oncolytic virus registered in Latvia. A female patient was diagnosed with stage IIIB melanoma in December 2012, over 9.4 years ago. After the first excision and re-excision, the patient had several recurrences and disease progressions. After the patient had received surgical treatment in 2014, ECHO-7 virus oncolytic virotherapy was started. Since then, the patient has experienced only one more disease progression episode in May 2015 and has been stable for over 60 months. The patient has not received any other treatment than surgery and oncolytic virotherapy. No severe adverse events have been reported during virotherapy. The present case suggests that ECHO-7 virotherapy is an effective treatment of skin melanoma.