Figure 2 - available via license: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International
Content may be subject to copyright.
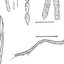
Schematic representation of polymorphisms of a fragment of 597 bp of the gene Cytochrome Oxidase I using Weblog. Shown are the sequences obtained from L. umbratilis collected in Recife, State of Pernambuco, Rio Preto da Eva and Manacapuru, State of Amazonas, Brazil. Font size is indicative of the frequency of a nucleotide at any given site. Fixed (black arrows)
Source publication
In South America, Lutzomyia umbratilis is the main vector of Leishmania guyanensis, one of the species involved in the transmission of American tegumentary leishmaniasis. In Brazil, L. umbratilis has been recorded in the Amazon region, and in the state of Pernambuco, Northeastern region, where an isolated population has been identified. This study...
Similar publications
The variation in wing morphological features was investigated using geometric morphometric technique of the Sand Fly from two Iraqi provinces Babylon and Diyala . We distributed eleven landmarks on the wings of Sand Fly species. By using the centroid size and shape together, all species were clearly distinguished. It is clear from these results tha...
Citations
... The omicron variant is the most mutated variant containing more than 60 mutations in its genome. In total, 32 of these mutations lie within the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein (41,42). The large number of mutations associated with the spike RBD domain can be related to infectivity rates, high transmission capacity, and rapid dispersal potential (26). ...
SARS-CoV-2 has caused a high number of deaths in several countries. In Brazil, there were 37 million confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 700,000 deaths caused by the disease. The population size and heterogeneity of the Brazilian population should be considered in epidemiological surveillance due to the varied tropism of the virus. As such, municipalities and states must be factored in for their unique specificities, such as socioeconomic conditions and population distribution. Here, we investigate the spatiotemporal dispersion of emerging SARS-CoV-2 lineages and their dynamics in each microregion from Sergipe state, northeastern Brazil, in the first 3 years of the pandemic. We analyzed 586 genomes sequenced between March 2020 and November 2022 extracted from the GISAID database. Phylogenetic analyses were carried out for each data set to reconstruct evolutionary history. Finally, the existence of a correlation between the number of lineages and infection cases by SARS-CoV-2 was evaluated. Aracaju, the largest city in northeastern Brazil, had the highest number of samples sequenced. This represented 54.6% (320) of the genomes, and consequently, the largest number of lineages identified. Studies also analyzed the relationship between mean lineage distributions and mean monthly infections, daily cases, daily deaths, and hospitalizations of vaccinated and unvaccinated patients. For this, a correlation matrix was created. Results revealed that the increase in the average number of SARS-CoV-2 variants was related to the average number of SARS-CoV-2 cases in both unvaccinated and vaccinated individuals. Thus, our data indicate that it is necessary to maintain epidemiological surveillance, especially in capital cities, since they have a high rate of circulation of resident and non-resident inhabitants, which contributes to the dynamics of the virus.
... In this study, it was only possible to infer the nucleotide divergence of only one gene fragment in the same way as a single morpho- (Figure 4). This connection can also be seen in Ny. umbratilis, in which populations from the north of the Amazon River are closely related to the Atlantic Forest population rather than other clusters in the Amazon region, suggesting an ancestral connection between these populations (Souza Freitas et al., 2015, 2016. In the case of Rondônia, the P. davisi MOTUs are in sympatry, and the possible absence of gene flow is not related to geographic barriers, indicating that they may already represent different species that could not yet be identified by morphology due to the absence of morphological disparity or the limited analysis of the morphological structures used in the description and identification of sand flies. ...
In this study, we analysed the molecular and morphometric differences of several populations of the putative sand fly vector Psychodopygus davisi (Root, 1934) (Diptera, Psychodidae, Phlebotominae) in Brazil. We amplified the 658 base pair fragments of the DNA barcoding region-cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (COI) gene-for 57 specimens of P. davisi and three specimens of Psychodopygus claustrei (Abonnenc, Léger & Fauran, 1979). We merged our data with public sequences of the same species available from GenBank. Then, the combined dataset-87 sequences and 20 localities-was analysed using population structure analysis and different species delimitation approaches. Geometric morphometry of wings was performed for 155 specimens of P. davisi populations from the North, Midwest and Southeast Brazilian regions, analysing the differences in centroid sizes and canonical variates. Molecular analysis indicated high intraspecific genetic distance values for P. davisi (maximum p distance = 5.52%). All algorithms identified P. davisi and P. claustrei as distinct molecular taxonomic units, despite the low inter-specific distance (p distance to the nearest neighbour = 4.79%). P. davisi sequences were split into four genetic clusters by population structure analysis and at least five genetic lineages using intermediate scenarios of the species delimitation algorithms. The species validation analysis of BPP strongly supported the five-species model in our data-set. We found high genetic diversity in this taxon, which is in agreement with its wide geographic distribution in Brazil. Furthermore, the wing analysis showed that specimens from the Southeast Region of Brazil are different from those in the North and the Mid-west. The evolutionary patterns of P. davisi populations in Brazil suggest the presence of
... The findings of this study on population structure (Figs. 2, 3; Table S3) revealed a deep and significant genetic split for L. umbratilis from the Brazilian Amazon, confirming the previous biological and molecular studies 33,35,38,40,41 . On the other hand, phylogenetic analyses with COI identified up to six groups, but only the groups represented by five (H67; H69 to H72) haplotypes from Pitinga (haplogroup V; Fig. 2) and the sample from Autazes were strongly supported in most of the analyses (Figs. 4, 5). ...
... On the other hand, Justiniano 39 observed discrete morphological differences in the immature stage, and in the number and size of the spines of armature of the female genital atrium between populations of these locations. The results of this study support the previous biological 38 and molecular studies 33,35,40,41 and, when taken together, it is possible to infer that the populations north and south of the Amazon River and interfluves represent distinct "species", which could have diverged more biological and molecular levels than morphologic 39 level, with implications distinct epidemiologic 13,37 . Genomics approach using loci involved in the different biologic aspects of L. umbratilis may clarify this issue. ...
Lutzomyia umbratilis is the main vector of Leishmania guyanensis in the Brazilian Amazon and in neighboring countries. Previous biological and molecular investigations have revealed significant differences between L. umbratilis populations from the central Brazilian Amazon region. Here, a phylogeographic survey of L. umbratilis populations collected from nine localities in the Brazilian Amazon was conducted using two mitochondrial genes. Statistical analyses focused on population genetics, phylogenetic relationships and species delimitations. COI genetic diversity was very high, whereas Cytb diversity was moderate. COI genealogical haplotypes, population structure and phylogenetic analyses identified a deep genetic differentiation and three main genetic groups. Cytb showed a shallower genetic structure, two main haplogroups and poorly resolved phylogenetic trees. These findings, allied to absence of isolation by distance, support the hypothesis that the Amazon and Negro Rivers and interfluves are the main evolutionary forces driving L. umbratilis diversification. The main three genetic groups observed represent three evolutionary lineages, possibly species. The first lineage occurs north of the Amazon River and east of Negro River, where Le. guyanensis transmission is intense, implying that L. umbratilis is an important vector there. The second lineage is in the interfluve between north of Amazon River and west of Negro River, an area reported to be free of Le. guyanensis transmission. The third lineage, first recorded in this study, is in the interfluve between south of Amazonas River and west of Madeira River, and its involvement in the transmission of this parasite remains to be elucidated.
... Studies suggested that there may be at least two cryptic species under the name Ny. umbratilis (Scarpassa & Alencar, 2012), which are presently not formally recognized. Interestingly, population structuring and phylogenetic data have shown that the Brazilian populations from Rio Preto da Eva (north of the Negro River; Amazonas state) and Recife (Pernambuco state) comprise a different clade when compared to a population from Manacapuru (south of the Negro River; Amazonas state) ( de Souza Freitas et al., 2015, 2016. Furthermore, some minor differences in the armature of genital atrium between specimens from Rio Preto da Eva and Manacapuru have been reported as well (Farias et al., 2015). ...
... It is interesting to note that populations of Ny. umbratilis recorded outside the Amazonian region are abundant in Atlantic forest remnants (Balbino et al., 2001(Balbino et al., , 2005a(Balbino et al., , 2005b. While these populations belong to a clade that includes a L. guyanensis-vector population from Rio Preto da Eva ( de Souza Freitas et al., 2015, 2016, the role of Ny. umbratilis as vector outside the Amazonian region remains unproven. More recently, Ny. umbratilis has been recorded in other non-Amazonian areas from Brazil (de Souza Freitas et al., 2018). ...
A species complex (= species group, species series) is an assemblage of species, which are related morphologically and phylogenetically. Recent research has revealed several arthropod vector species that were believed to be a single nominal species actually representing a group of closely related species, which are sometimes morphologically indistinguishable at one or more developmental stages. In some instances, differences in terms of vector competence, capacity, or both have been recorded. It highlights the importance of detecting and studying species complexes to improve our understanding of pathogen transmission patterns, which may be vectored more or less efficiently by different species within the complex. Considering more than 540 species, about one-third of the phlebotomine sand flies in the New World present males and/or females morphologically indistinguishable to one or more species. Remarkably, several of these species may act in transmission of pathogenic agents. In this article, we review recent research on species complexes in phlebotomine sand flies from the Americas. Possible practical implications of recently acquired knowledge and future research needs are also discussed.
... The northeast and northern regions continue to report a large number of CL cases [9,10]. Studies show that the presence of settlements in forested areas and environmental degradation are important drivers of the rising number of leishmaniasis cases since they can contribute to the adaptation and expansion of sand fly vectors in areas of human intervention, whether in urban or periurban areas [11][12][13][14]. ...
Background
Phlebotomines are a group of insects which include vectors of the Leishmania parasites that cause visceral leishmaniasis (VL) and cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), diseases primarily affecting populations of low socioeconomic status. VL in Brazil is caused by Leishmania infantum , with transmission mainly attributed to Lutzomyia longipalpis , a species complex of sand fly, and is concentrated mainly in the northeastern part of the country. CL is distributed worldwide and occurs in five regions of Brazil, at a higher incidence in the north and northeast regions, with etiological agents, vectors, reservoirs and epidemiological patterns that differ from VL. The aim of this study was to determine the composition, distribution and ecological relationships of phlebotomine species in an Atlantic Forest conservation unit and nearby residential area in northeastern Brazil.
Methods
Centers for Disease Control and Shannon traps were used for collections, the former at six points inside the forest and in the peridomestic environment of surrounding residences, three times per month for 36 months, and the latter in a forest area, once a month for 3 months. The phlebotomines identified were compared with climate data using simple linear correlation, Pearson’s correlation coefficient and cross-correlation. The estimate of ecological parameters was calculated according to the Shannon-Wiener diversity index, standardized index of species abundance and the dominance index.
Results
A total of 75,499 phlebotomines belonging to 11 species were captured in the CDC traps, the most abundant being Evandromyia walkeri , Psychodopygus wellcomei and Lu. longipalpis . Evandromyia walkeri abundance was most influenced by temperature at collection time and during the months preceding collection and rainfall during the months preceding collection. Psychodopygus wellcomei abundance was most affected by rainfall and relative humidity during the collection month and the month immediately preceding collection time. Lutzomyia longipalpis abundance showed a correlation with temperature and the rainfall during the months preceding collection time. The Shannon trap contained a total of 3914 phlebotomines from these different species. Psychodopygus wellcomei , accounting for 91.93% of the total, was anthropophilic and active mainly at night.
Conclusions
Most of the species collected in the traps were seasonal and exhibited changes in their composition and population dynamics associated with local adaptions. The presence of vectors Ps. wellcomei and Lu. longipalpis underscore the epidemiological importance of these phlebotomines in the conservation unit and surrounding anthropized areas. Neighboring residential areas should be permanently monitored to prevent VL or CL transmission and outbreaks.
... Its principal vector is Lu. Umbratilis phleobotomine 30,37 , which is found in the early hours of the morning in moist soil environments such as the trunks of large trees 38 . One unique feature of phlebotomine is the high number of bites it causes in individuals. ...
INTRODUCTION:
Brazil has a high number of cases of American cutaneous leishmaniasis (ACL) in the north and northeast regions. Therefore, continuous surveillance of environmental and socioeconomic factors in endemic areas is needed to develop strategic control measures. This study aimed to describe the clinical and epidemiological profiles of patients with ACL.
METHODS:
All patients were from the states of Amazonas and Pernambuco, and examinations were carried out between 2015 and 2018. All patients had a clinical and epidemiological history compatible with ACL after positive diagnostic tests. Information obtained from medical records included gender, employment activity, level of education, age, and number and sites of lesions.
RESULTS:
A total of 213 patients were included, of whom 30.98% were female and 69.02% were male. The main employment activity was agriculture (27.56%). The most common level of education was elementary (62.42%). The average age was approximately 39 years. The majority of the patients presented only with one lesion (54.87%), and legs/feet were the most commonly affected area (48.25%), followed by the arms/hands (44.75%).
CONCLUSIONS:
These data demonstrated that irrespective of the patients’ places of origin, interventions need to be focused on men of economically productive age, in view of the high risk of exposure to the vector in this group. Education activities need to be directed to farmers about the importance of protection against ACL vectors during work. Such information must also be directed to employers as a way of implementing and maintaining appropriate working conditions and stepping up vector control.
... intermedia, whereas L. panamensis comes from the Colombian Andean mountain's region where the main vector is Lu. gomezi, and L. guyanensis strain was isolated in the Amazon region where it is mainly transmitted by Lu. umbratilis [73][74][75]. Such distinct landscapes exhibit different flora and fauna for sandflies feeding and those distinct ecological scenarios should influence the preference for a particular metabolic pathway in parasites. ...
Leishmania species are responsible for a broad spectrum of diseases, denominated Leishmaniasis, affecting over 12 million people worldwide. During the last decade, there have been impressive efforts for sequencing the genome of most of the pathogenic Leishmania spp. as well as hundreds of strains, but large-scale proteomics analyses did not follow these achievements and the Leishmania proteome remained mostly uncharacterized. Here, we report a comprehensive comparative study of the proteomes of strains representing L. braziliensis, L. panamensis and L. guyanensis species. Proteins extracted by SDS-mediated lysis were processed following the multi-enzyme digestion-filter aided sample preparation (FASP) procedure and analysed by high accuracy mass spectrometry. “Total Protein Approach” and “Proteomic Ruler” were applied for absolute quantification of proteins. Principal component analysis demonstrated very high reproducibility among biological replicates and a very clear differentiation of the three species. Our dataset comprises near 7000 proteins, representing the most complete Leishmania proteome yet known, and provides a comprehensive quantitative picture of the proteomes of the three species in terms of protein concentration and copy numbers. Analysis of the abundance of proteins from the major energy metabolic processes allow us to highlight remarkably differences among the species and suggest that these parasites depend on distinct energy substrates to obtain ATP. Whereas L. braziliensis relies the more on glycolysis, L. panamensis and L. guyanensis seem to depend mainly on mitochondrial respiration. These results were confirmed by biochemical assays showing opposite profiles for glucose uptake and O2 consumption in these species. In addition, we provide quantitative data about different membrane proteins, transporters, and lipids, all of which contribute for significant species-specific differences and provide rich substrate for explore new molecules for diagnosing purposes. Data are available via ProteomeXchange with identifier PXD017696.
... Although Bergmann's rule (linked to temperature) has been reported in some sandflies species (Dujardin and Pont 2004;Prudhomme et al. 2016;Oguz et al. 2017), our results are according with this described by Marcondes et al. 1999. On the other hand, our results suggest a pattern of local genetic divergence within a province, as has been documented in other Phlebotominae species (Rangel et al. 1996;Dujardin et al. 1999;Margonari et al. 2004;Ranasinghe et al. 2012;Florin and Rebollar-Téllez 2013;Arrivillaga et al. 2003;De Souza Freitas et al. 2015). It is important to evaluate the genetic structure of populations assessed here and if there is a correspondence between the morphological differentiation and the existence of genetic lineages. ...
Lutzomyia cruciata (Diptera: Phlebotominae) is an important Leishmania vector with wide distribution in America. However, geographical patterns of morphological variation of populations along its longitudinal and latitudinal distribution are still unknown. In this work, we quantified morphological variation and disparity in 243 specimens (females) from nine sample groups of Lu. cruciata from two biogeographical provinces in Mexico: Veracruzan Province (five groups) and Yucatan Peninsula Province (four groups). We registered two linear morphometric data of a reproductive structure (spermatheca) and one landmark configuration for wing shape. Our questions were if intraspecific morphological variation and disparity are related to contrasting environmental factors in these two provinces. First, our results from canonical variates analyses of the spermatheca and wing shape revealed more differences among groups of specimens within a biogeographic province than between. Second, our regression analyses revealed that morphometric variation is weakly related to 20 environmental variables considered for the two biogeographic provinces. Levels of morphological disparity in the spermatheca and wing shape within the two provinces are the same regardless of environmental homogeneity in the Yucatan Province or heterogeneity in the Veracruzan Province. These patterns of morphological variation and disparity weakly correlated with environmental variables suggest that intraspecific variation in Lu. cruciata is not clinal within a province. Subsequent investigations will be required to elucidate suspected correlations of local discontinuous phenotypes with genetic divergence within a biogeographical province.
... The biological similarity among geographically isolated populations can lead to similar vector patterns (Souza et al. 2015), that is, exhibit the same permissive or specific condition to Leishmania species circulating in the region. In this study, the sampled sites are located in a region with case reports of human Leishmaniasis (Ortega-Grillasca and Vidal-Antonio, 1990); however, aspects of the ecology and biology of sandflies vectors and species or strains of Leishmania are unknown. ...
The presence of Lutzomyia (Tricholateralis) cruciata (Coquillett 1907) species complex has been suggested by morphological analysis of eggs and genetic studies of females. The present work aimed to compare the diversity in morphology of four populations of Lu. cruciata from the Coast of Chiapas, Mexico, using traditional (TM) and geometric (GM) methods. Several morphological characteristics that were analyzed provided consistency to differentiate at least, three populations of Lu. cruciata. Both methods were effective to detect morphological differences associated with the geographical sites of capture. In both sexes, three and four groups were detected by TM and GM, respectively. These results suggest marked morphological differences in both sexes of Lu. cruciata that make these methods potentially useful to identify the geographical origin of any specimen of this species captured in the study region. Although the results produced by both methods are coincident, geometric morphometrics turned out to be most advantageous with respect to traditional morphometry, since the latter requires more time and effort. The consistency of our results shows that the variability of environmental conditions on the coast of Chiapas determines a high degree of phenotypic plasticity in Lu. cruciata, with the possibility of prezygotic isolation and the formation of species complex. © The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Entomological Society of America.
All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: [email protected]
... In sand flies, this technique has been employed in populational and taxonomic studies using mainly the wing (De la Riva et al. 2001;Prudhomme et al. 2012;Godoy et al. 2014;Freitas et al. 2015). Although they prove to be elucidative in some cases, wing shape analyses have some limitations, as sand flies have reduced wing venation. ...
Almost 30% of female American sand flies are morphologically indistinguishable from one another. These females belong to species-complexes or groups with closely related species, making species-level identification difficult or even impossible. This fact has implications for public health since several of these groups include species which are vectors of human pathogens. Thus, new tools are needed to minimize species-level identification problems. In this context, our research sought to use geometric morphometry in the study of the head of females of closely related species of the genus Psychodopygus, Chagasi series, which includes the following species: P. chagasi, P. complexus, P. squamiventris maripaensis, P. squamiventris squamiventris, and P. wellcomei. We have used ten landmarks distributed on the head of these species. All species were clearly distinguished using the centroid size and shape together. These results highlight the head analysis as an effective tool for future geometric morphometry studies in sand flies.