Figure 1 - uploaded by Jie Yang
Content may be subject to copyright.

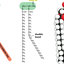
Balanced optical heterodyne detection system. PBS: Polarization Beam Splitter; 2 : 2 wave plate; M: Mirror; L: Lens; APD: Avalanche Photo Diode; SA: Spectrum Analyzer; OSC: Oscilloscope. AOM: Acoustic Optical Modulator; TC: Temperature Controller; LDC: Laser Diode Controller
Source publication
A semiclassical approach is used to calculate the principle for
heterodyne detection utilizing two optical detectors. These calculations
show that excess-noise in the local-oscillator can be canceled and the
balanced-detector optical heterodyne detection requires less local
oscillator power compared with the traditional single-detector optical
hete...
Contexts in source publication
Context 1
... layout of the optical system is shown in Figure 1. This system is designed to detect a pW scale weak optical signal. ...
Context 2
... part one, a Littrow semiconductor laser is established to modulate a near 852nm single longitudinal mode laser. A FP laser diode (b in Figure 1) packed in a laser diode mount (a in Figure 1) generates about 5mW continuous-wave light near 850 nm. a is TCLDM9 laser diode mount to pack b, which is a FP laser diode generates about 5mW of continuous- wave light near 850nm; c is a lens to make the laser emitted from FP diode collimated in a long optical path; d and e are separately a wave plate and a diffraction grating, for the reason that the grating efficiency is strongly related to light polarization. The mounting angle of the grating is extremely essential to the system, cause only the grating at the right angle could guarantee the -1 order radiation to feedback to the diode thus to form a Littrow semiconductor laser, the zero order radiation is the emitting light. ...
Context 3
... part one, a Littrow semiconductor laser is established to modulate a near 852nm single longitudinal mode laser. A FP laser diode (b in Figure 1) packed in a laser diode mount (a in Figure 1) generates about 5mW continuous-wave light near 850 nm. a is TCLDM9 laser diode mount to pack b, which is a FP laser diode generates about 5mW of continuous- wave light near 850nm; c is a lens to make the laser emitted from FP diode collimated in a long optical path; d and e are separately a wave plate and a diffraction grating, for the reason that the grating efficiency is strongly related to light polarization. The mounting angle of the grating is extremely essential to the system, cause only the grating at the right angle could guarantee the -1 order radiation to feedback to the diode thus to form a Littrow semiconductor laser, the zero order radiation is the emitting light. ...
Context 4
... we used APD1 (in Figure 1) to detect the weak attenuated optical signal, the reflection rate and transmission rate of PBS4 is 0.498 and 0.467, and the sensitivity of APD1 is 46.5 mV/μW . We calibrated four attenuators with different optical density, allowing them to attenuate its optical density to its 1 Then the two optical beam were mixed into one beam at PBS3, and then interference after passing through 2 , the calculated 1MHz beat signal detected by APD1 should be 6 640 2.1 10 0.498 46.5=0.83mV ...
Similar publications
This talk will describe modified uni-traveling carrier photodiodes (MUTCs) that have achieved high RF output power and high saturation current. Discrete photodiodes, 4×1 phase matched arrays, and balanced detectors will be discussed.
Citations
Large field of view of the coherent receiver requires large detector photosurface area, but with the increase of detector photosurface area, the SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) of the coherent receiver will decline. A balanced photodetection with large photosurface APD can not only increase the angular field of view, and can guarantee the detection sensitivity, which satisfy the coherent receiver’s requirements. An experimental measurement of a balanced APD photodetection is reported.